What is OCR?
Discover the transformative power of OCR, simplifying text conversion from images. From personal archiving to revolutionizing industries, OCR enhances productivity, streamlines workflows, and drives innovation across sectors.
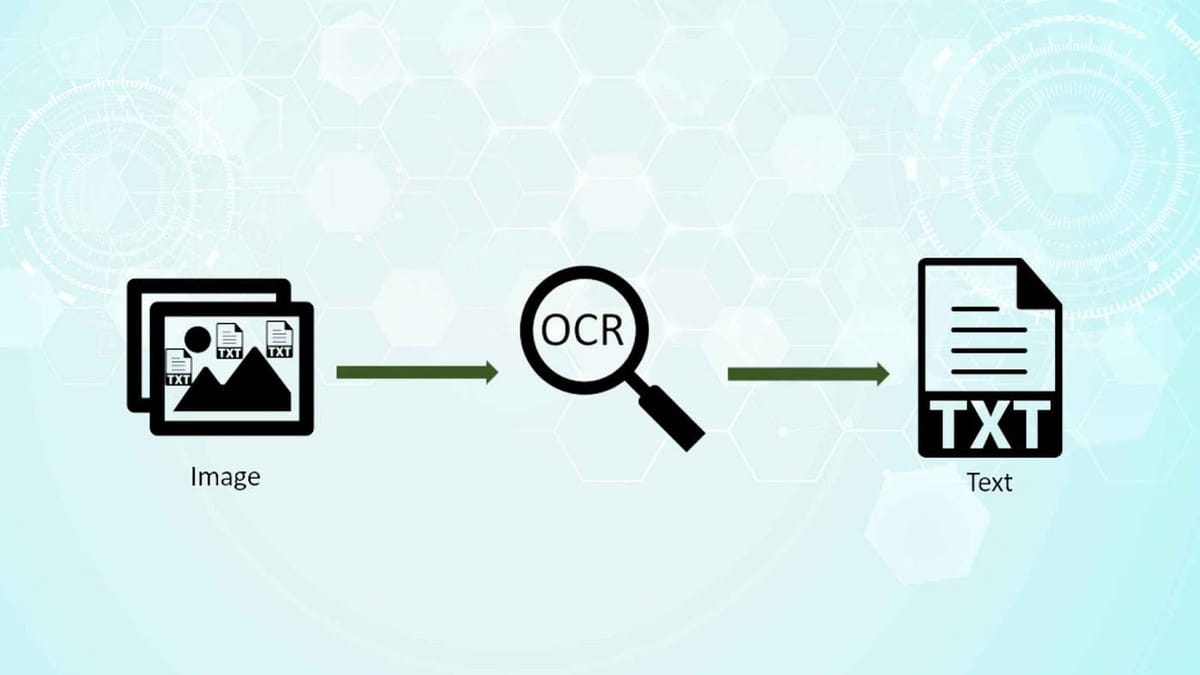
What is OCR?
Optical Character Recognition (OCR), also known as text recognition, is a groundbreaking technology transforming document images into editable text or digital files, making them machine-readable. Imagine scanning a receipt on your computer; initially saved as an image.
But with OCR, this image metamorphoses into an editable text document, enabling easy editing and searchability. This streamlined process eliminates the need for manual data entry, significantly enhancing productivity.
OCR software utilizes advanced techniques like intelligent character recognition (ICR), often powered by artificial intelligence (AI). These methods empower OCR to identify languages, handwriting styles, and even reconstruct fragmented text. Essentially, OCR democratizes access to information by making static content adjustable and searchable, much like word processor documents.
It operates akin to a digital copier, revolutionizing our interaction with printed text, optimizing workflows, and broadening horizons in document management.
Why OCR is important?
OCR stands as a pivotal tool in both personal and professional domains, serving as a vital resource for converting handwritten notes, paper documents like receipts, recipes, contracts, and legal documents, along with various text-containing images into digital formats. This streamlined conversion facilitates effortless editing and archival of personal documents.
In the business landscape, where workflows rely heavily on data extracted from printed materials, OCR emerges as a cornerstone. Paper forms, invoices, scanned legal documents, and printed contracts constitute integral components of business processes. Yet, managing copious amounts of paperwork poses challenges in terms of time and space efficiency.
While transitioning to paperless document management is optimal, the process of scanning documents into image formats presents its own set of hurdles. Manual intervention in this process often proves to be laborious and time-consuming.
Moreover, digitizing document content results in image files with embedded text, which cannot be processed by standard word processing software in the same manner as text documents. This is where OCR technology shines, transforming text images into analyzable text data that can seamlessly integrate with other business software.
Leveraging OCR-generated data enables businesses to conduct comprehensive analytics, streamline operations, automate processes, and ultimately enhance productivity, making it an indispensable asset in modern business operations.
How does OCR work?
The OCR engine or OCR software works by using the following steps:
Image acquisition:
The input may consist of images or image-only PDF documents. Through meticulous analysis, the OCR software discerns between light areas, designated as background, and dark areas, identified as text.
Any deviations in the classification process could significantly impair the OCR performance.
Preprocessing:
The OCR software first cleans the image and removes errors to prepare it for reading. These are some of its cleaning techniques:
• Rectifying image alignment issues through deskewing or tilting.
• Removing digital image spots and smoothing text image edges via despeckling.
• Eliminating extraneous elements such as boxes and lines from the image.
• Implementing script recognition to support multi-language OCR technology.
Text recognition:
Text recognition in OCR involves two primary algorithms: pattern matching and feature extraction.
Pattern matching isolates character images, known as glyphs, and compares them with stored glyphs of similar font and scale. This method relies on pattern recognition, functioning effectively with scanned documents typed in known fonts.
On the other hand, feature extraction decomposes glyphs into elements like lines, closed loops, and intersections. These features are then utilized to identify the best match or nearest neighbor among the stored glyphs.
Postprocessing:
Following analysis, the system transforms the extracted text data into a digital file format. Certain OCR systems offer the capability to generate annotated DOC or PDF files, encompassing both the original and processed versions of the scanned document.
The history of optical character recognition
The genesis of this transformative technology traces back to 1974 when Ray Kurzweil founded Kurzweil Computer Products, Inc. This groundbreaking innovation had the capacity to recognize text across a vast array of fonts.
Kurzweil envisioned its primary utility as an assistive tool for the visually impaired, leading to the creation of a reading machine capable of converting text into speech format. In 1980, he astutely sold his company to Xerox, recognizing their keen interest in commercializing paper-to-computer text transformation.
Although initially underappreciated, the technology gained traction in the early 1990s, particularly for digitizing historical newspapers. Since then, OCR has undergone significant advancements, culminating in near-perfect accuracy in text conversions today.
Advanced OCR methods have revolutionized document processing workflows, automating tasks that were once labor-intensive and error-prone. Prior to the availability of this software, manual retyping of documents was the norm, consuming substantial time, effort, and resources, with an elevated risk of content errors.
Presently, OCR is ubiquitous and continues to enhance efficiency across personal and professional domains.
What are the benefits of OCR?
The primary benefit of OCR technology lies in its ability to streamline the data entry process, facilitating effortless text searches, editing, and storage. By employing OCR, businesses and individuals can conveniently store files on various devices, ensuring constant access to all documentation.
Key benefits of utilizing OCR technology include:
- Conversion of handwritten notes or paper documents into digital format for easy searching, editing, and archiving of essential information.
- Word recognition capabilities for language learning purposes.
- Cost reduction through enhanced efficiency in document management processes.
- Acceleration of workflow and operational efficiency.
- Automation of document routing and content processing tasks.
- Centralization and secure storage of data, mitigating risks associated with physical document storage.
- Integration with other AI applications, such as license plate recognition, identification of brand logos in social media posts, and detection of product packaging in advertising images and more.
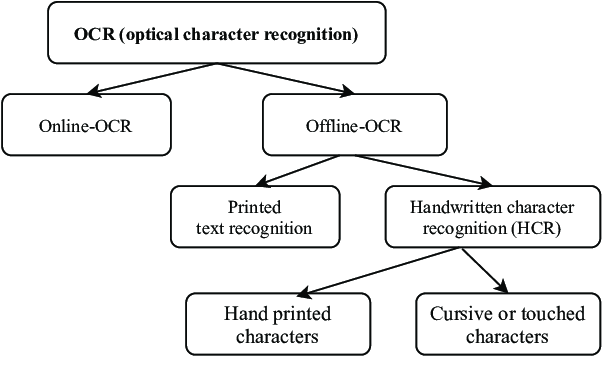
What are the types of OCR?
From a technical standpoint, OCR can be categorized into online and offline types. In contemporary settings, Online OCR often relies on extensive neural networks, resulting in superior accuracy performance, while offline OCR is typically utilized for embedded applications.
In terms of character recognition, there are two main categories: printed text recognition and handwritten character recognition (HCR). Handwriting OCR, capable of deciphering both printed characters and cursive writing, presents a significant challenge, particularly in multilingual contexts.
What are OCR user cases?
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) serves essential purposes by converting text from images, catering to a broad range of user needs.
For personal use:
· Saving handwritten notes, screenshots, and hard copies like receipts, recipes, legal documents, and medical records.
· Facilitating education and language learning by converting text from books into searchable digital formats.
· Allowing for the swift conversion of mathematical equations into LaTeX format, enabling computer searchability and solvability.
For businesses:
Banking:
OCR is utilized in the banking sector to process and verify paperwork for deposit checks, loan documents, and financial transactions. This verification process helps mitigate fraud risks, enhance transaction security, and build trust among customers, thereby enhancing the bank's reputation.
Healthcare:
In the healthcare industry, OCR is employed to process patient records, including tests, treatments, and insurance payments. This technology aids in keeping records current, reducing manual workload, and streamlining workflow processes.
Logistics:
Logistics companies use OCR technology to efficiently manage invoices, package labels, and other documents. By automating document processing, OCR improves accuracy, reduces errors, and enhances overall efficiency in logistics operations.
Travel:
The travel industry relies on OCR technology to expedite passport and travel application processes, improving safety and data security. OCR eliminates manual errors in authentication and speeds up information processing, resulting in better customer experiences and increased automation in travel services.
Government:
OCR plays a critical role in streamlining information processing in various government sectors, from licensing to voter registration. By automating data verification, OCR enhances efficiency and accuracy in government operations.
Food Industry:
OCR technology, powered by machine learning, aids the food industry in digitizing menus and creating databases of recipes with detailed nutritional information. This advancement improves customer experiences and enhances operational efficiency in food-related businesses.
Retail:
OCR technology enhances the retail sector by facilitating the scanning and retrieval of relevant data from payment bills, invoices, packing lists, and purchase orders. By providing structured data formats for easy access and end-to-end data processing, OCR improves efficiency and productivity in retail operations.
Best OCR software
- Grabtext.ai
- Microsoft
- Google Lens
- Apple Note
- Pen to print
- Adobe OCR
- OmniPage Ultimate
- Abbyy finereader
- Readiris
Conclusion
In conclusion, Optical Character Recognition (OCR) stands as a transformative technology that revolutionizes the conversion of text from images, catering to a wide spectrum of user needs across personal and professional domains.
OCR facilitates seamless data entry processes, enabling effortless text searches, editing, and storage. It empowers individuals and businesses to archive handwritten notes, paper documents, and various text-containing images in digital formats, enhancing accessibility and productivity.
From banking to healthcare, logistics to travel, and government to retail, OCR finds applications in diverse industries, streamlining operations, reducing manual workload, and enhancing efficiency. By automating document processing tasks and providing structured data formats, OCR drives operational excellence and fosters innovation.
In essence, OCR plays a pivotal role in modern information management, empowering users to unlock the full potential of their data, streamline workflows, and drive business success in today's digital age.
FAQ:
What is OCR used for?
OCR is used to convert scanned documents and images into editable text, enhancing digitization and data accessibility.
What does OCR stand for?
OCR stands for Optical Character Recognition.
How to OCR a pdf?
To OCR a PDF, use specialized software or online tools that support OCR. Upload the PDF to the chosen platform, initiate the OCR process, and the tool will convert the scanned or image-based text within the PDF into editable and searchable content.
What is OCR scanning?
OCR scanning is the use of technology to convert printed or handwritten text from images or scanned documents into editable and searchable text.



